Restrict Access to AWS Elasticsearch Through VPC
Dec 2, 2015
Update: AWS has officially released support for VPCs in AWS Elasticsearch.
On the 1st of October, 2015, Amazon introduced an Elasticsearch-as-a-service offering similar to Elastic.co's Found called AWS Elasticsearch Service. It lets you easily deploy an Elasticsearch cluster that is redundant, scalable, and highly-available. Sounds too good to be true, right? Here's how Amazon describes their new service:
Amazon Elasticsearch Service is a managed service that makes it easy to deploy, operate, and scale Elasticsearch in the AWS Cloud. Elasticsearch is a popular open-source search and analytics engine for use cases such as log analytics, real-time application monitoring, and click stream analytics.
Benefits
There are several reasons to use AWS Elasticsearch:
- Avoid the headache of setting up and scaling Elasticsearch on your own
- Easily scale the cluster on demand by modifying the number of nodes and their underlying EC2 instance type
- Enable dedicated master nodes for improved reliability
- Back up your data using automated or manual snapshots
No VPC Support!
However, there's a major problem with AWS Elasticsearch as of the date of this post -- it lacks VPC support. That means your AWS Elasticsearch endpoint will be publicly-accessible at all times, and that the only way to limit access to it is by:
- Creating an IAM user, configuring the Elasticsearch cluster to trust it, and signing all requests with its credentials
- Whitelisting a set of IPs that can access the Elasticsearch cluster
Option 1 is pretty much off the table, since no Elasticsearch library supports IAM request signing as of today, and modifying the underlying request code to add the relevant headers and parameters is unrealistic, especially if you use multiple Elasticsearch libraries to interact with your cluster.
Option 2 has some potential, however, the time it takes to update the IP whitelist is extremely slow -- ~10 minutes, more or less. This makes it impossible to whitelist servers that are launched on-demand in an auto-scaling scenario.
The Workaround
There's a really simple workaround that can be taken advantage of while we wait for AWS to implement VPC support for Elasticsearch:
You can limit cluster access to a single EC2 server in your VPC with a public Elastic IP, run
nginxon it, and configure it to forward requests to the Elasticsearch endpoint. You can then configure that server's security groups to only allow HTTP access from within the VPC.
This is a decent workaround, and as we'll see later on, can also be scaled, if necessary.
Set up an EC2 Proxy Server
This is pretty straightforward. Launch a new EC2 instance (I prefer Ubuntu 14.04 LTS) within your VPC and assign a Public IP to it.

SSH into it and run the following commands to install nginx:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install nginxConfigure Nginx
Next, we'll need to configure Nginx so that it forwards traffic to our Elasticsearch cluster. Let's start off by removing the default configuration file:
sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultNext, create a new file in /etc/nginx/sites-available/ called elasticsearch and open it with nano:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/elasticsearchPaste the following code in the file and make sure to change https://elastic-endpoint.amazonaws.com to your Elasticsearch cluster endpoint URL:
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_pass https://elastic-endpoint.amazonaws.com;
}
}The proxy_pass declaration configures Nginx to act as a reverse proxy. It will forward all incoming requests on port 80 of your server to your Elasticsearch cluster.
Next, we need to symlink our configuration to sites-enabled for it to be used by Nginx, since it's currently in sites-available:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/elasticsearch /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/elasticsearchApply the Configuration
Let's restart Nginx so that it loads our configuration:
sudo service nginx restartRestrict Access to the Cluster
Finally, head over to your AWS Elasticsearch cluster configuration and click Modify access policy. Then, click on Select a template and select Allow access to the domain from specific IP(s):
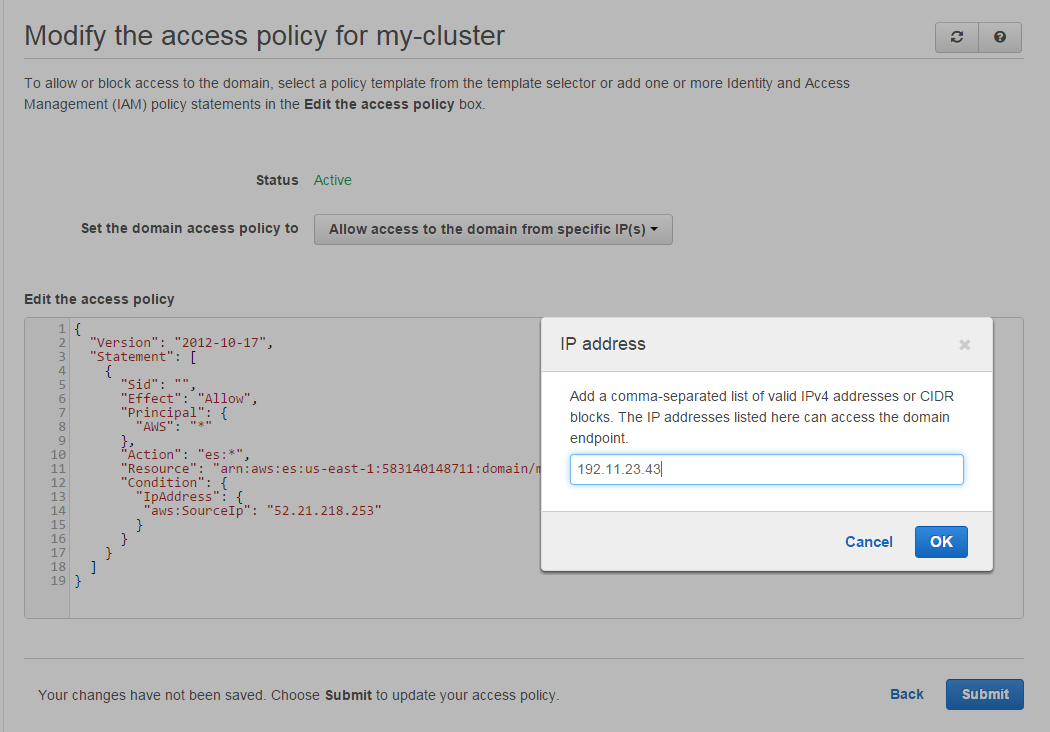
Enter the EC2 instance's Elastic IP, click OK, Submit, and you should be good to go. When your Elasticsearch domain's status changes back to Active, the policy will be in effect and the public endpoint you once had will no longer be accessible directly.
Scalability
One could argue that this solution creates a single point-of-failure for your Elasticsearch cluster. This is true, and to overcome this, you can simply repeat the process X more times to scale the gateway (set up X more instances, configure them with nginx, and whitelist their IPs in the cluster access policy). You can then link them to an EC2 Load Balancer to create a secure, highly-available gateway to your cluster through your VPC. The only drawback is that it is not possible to auto-scale this gateway (since it takes too long to update the AWS Elasticsearch IP whitelist).
That's it!
You have successfully restricted all access to your AWS Elasticsearch cluster through a VPC. This is a fine workaround until AWS officially supports VPCs in AWS Elasticsearch. Don't forget to update your servers with the new endpoint URL (the EC2 server's private IP address), otherwise, they won't be able to connect to Elasticsearch! Also, if you prefer, you can create a DNS record (e.g. elasticsearch.example.com) to point to your EC2 server's IP, and then use that as your endpoint URL.
